Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling can significantly limit your mobility and quality of life. Traditionally, joint conditions were diagnosed and treated with large incisions and lengthy recovery times. But with advancements in medical technology, procedures like arthroscopy have revolutionized orthopedic care.
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to diagnose and treat joint problems. It’s commonly used for knees, shoulders, hips, elbows, and ankles. The procedure is known for its smaller incisions, faster recovery, and reduced post-surgical complications compared to open surgery.
In this blog, we’ll explain what arthroscopy is, how it works, its benefits, risks, and who can benefit from this procedure.
What is Arthroscopy?
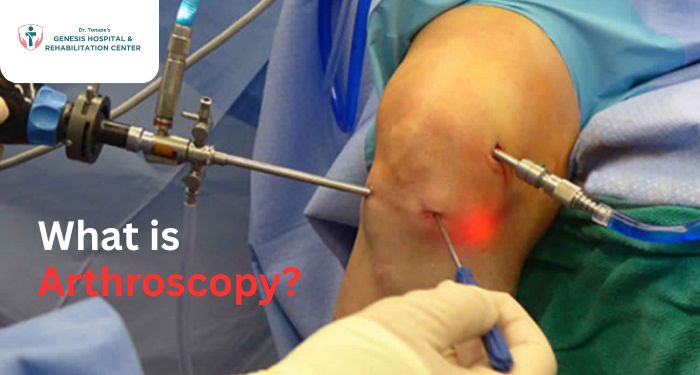
The term arthroscopy comes from the Greek words “arthro” (joint) and “skopein” (to look). It literally means “to look inside the joint.” During the procedure, an orthopedic surgeon inserts a small camera called an arthroscope into the joint through a tiny incision. This camera displays images on a screen, allowing the surgeon to examine the inside of the joint with precision.
Through additional small incisions, the surgeon can also insert specialized instruments to perform surgical tasks such as:
-
Removing damaged cartilage
-
Repairing ligaments or tendons
-
Removing bone spurs or loose fragments
-
Treating joint inflammation
Which Joints Can Be Treated with Arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy is commonly performed on:
-
Knees (most common)
-
Shoulders
-
Elbows
-
Hips
-
Wrists
-
Ankles
Conditions Treated with Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy can be used for both diagnosis and treatment of various joint conditions, including:
-
Torn meniscus in the knee
-
ACL or PCL ligament injuries
-
Rotator cuff tears
-
Frozen shoulder
-
Loose cartilage or bone fragments
-
Synovitis (inflammation of the joint lining)
-
Labral tears (hip or shoulder)
-
Arthritis-related damage
-
Recurrent joint dislocations
Benefits of Arthroscopy
Compared to traditional open surgery, arthroscopy offers several key advantages:
-
Minimally Invasive
Small incisions result in less tissue damage and scarring. -
Faster Recovery Time
Most patients can return to light activity within days or weeks. -
Reduced Pain and Swelling
Less trauma to surrounding tissues results in lower postoperative pain. -
Lower Infection Risk
Small wounds are easier to manage and heal faster. -
Outpatient Procedure
Many arthroscopic surgeries are done on a same-day basis.
Who is a Good Candidate for Arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy is ideal for patients who:
-
Have persistent joint pain or swelling
-
Have not responded well to medications or physical therapy
-
Need a confirmed diagnosis of a joint issue
-
Want a quicker recovery with minimal disruption to daily life
However, it may not be suitable for people with severe joint arthritis or deformities, in which case joint replacement may be considered.
What to Expect During the Procedure
Arthroscopy is typically performed under general or regional anesthesia. The surgery usually takes between 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the joint and condition being treated.
Most patients go home the same day. Recovery involves rest, physical therapy, and following post-op instructions carefully. Most people return to work or light activity within a few days to weeks, though full recovery can take longer depending on the type of repair done.
Are There Any Risks?
Arthroscopy is generally safe, but as with any surgery, it carries some risks:
-
Infection
-
Bleeding
-
Blood clots
-
Nerve or tissue damage
-
Joint stiffness or swelling
Choosing an experienced orthopedic surgeon greatly reduces these risks.
Conclusion
Arthroscopy has transformed orthopedic care with its precision, speed, and minimally invasive approach. Whether you’re an athlete with a torn ligament or someone dealing with long-term joint discomfort, arthroscopy offers a safe and effective way to diagnose and treat joint problems.
If you’re suffering from unexplained joint pain or injury, consult an experienced orthopedic specialist. Early evaluation and proper treatment can help restore movement, reduce pain, and improve your quality of life.